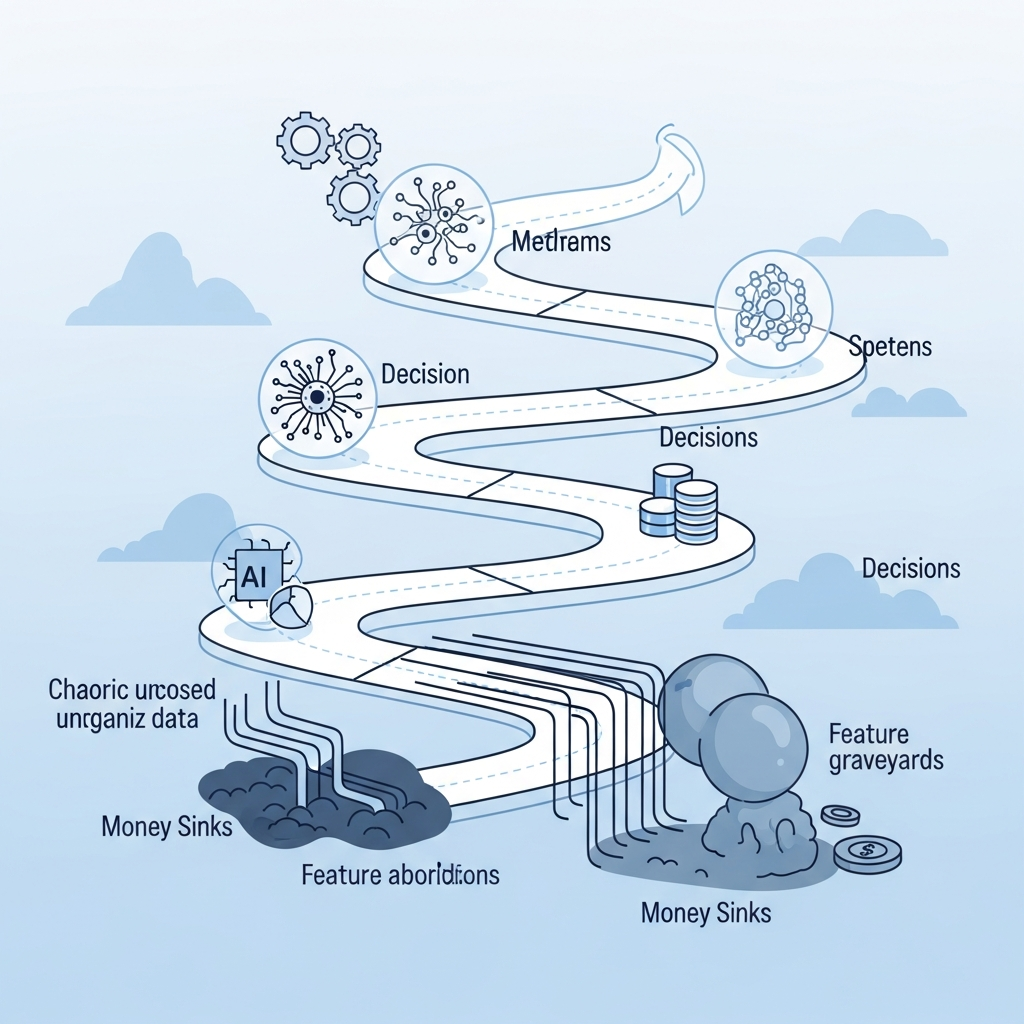
Unlock Generative AI’s Potential: Avoid These Common Mistakes
Generative AI is transforming industries, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and creativity. From drafting content to generating code and designing products, its capabilities are vast and growing. However, like any powerful technology, harnessing Generative AI effectively requires a strategic approach. Many organizations and individuals jump in without fully understanding the nuances, leading to wasted resources, suboptimal results, or even outright failure.
This post highlights five critical mistakes commonly made when working with Generative AI and provides actionable advice on how to navigate these challenges, ensuring your AI initiatives deliver real value.
1. Failing to Define Clear Business Objectives (Going Too Big or Too Small)
One of the most frequent missteps is treating Generative AI as a solution looking for a problem. Without a well-defined business goal, projects can quickly become unfocused, overly ambitious, or too trivial to yield significant ROI.
What to do instead:
- Start with the ‘Why’: Before even thinking about models or prompts, clearly articulate the specific business challenge you’re trying to solve or the opportunity you want to seize.
- Scope Appropriately: Avoid the trap of ‘going too big’ by attempting to solve all problems at once. Begin with a minimum viable product (MVP) that addresses a specific pain point. Conversely, don’t ‘go too small’ by tackling issues with negligible impact. Aim for a project that demonstrates clear value and can scale.
- Quantify Success: Establish measurable KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) for your AI project. How will you know if it’s successful? What metrics will you track?
2. Neglecting Data Quality and Preparation
Generative AI models, especially those using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), are heavily reliant on the quality and relevance of the data they process. Assuming that a powerful model can compensate for poor input data is a recipe for disaster – known as “garbage in, garbage out.”
What to do instead:
- Prioritize Data Strategy: Invest time and resources in curating, cleaning, and structuring your proprietary data. For RAG systems, ensure your knowledge base is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to the queries your AI will handle.
- Establish Data Governance: Implement processes for data validation, version control, and access management. This ensures data integrity and consistency over time.
- Vectorize Thoughtfully: If using embeddings for RAG, choose appropriate chunking strategies and embedding models that capture the semantic meaning of your data effectively.
3. Underestimating the Complexity of Advanced AI Architectures (e.g., RAG)
While frameworks like RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) offer immense potential for grounding Generative AI models in factual, up-to-date information, simply implementing the basic architectural pattern isn’t enough. Many believe that “RAG + a simple prompt” is a complete solution, overlooking the intricate details required for robust performance.
What to do instead:
- Deep Dive into RAG Components: Understand that RAG involves more than just a vector database and a large language model. It includes intelligent retrieval strategies, reranking, query expansion, and careful prompt construction that integrates retrieved context seamlessly.
- Iterate and Optimize: Continuously evaluate and refine your retrieval process, chunking methods, embedding models, and the prompt’s interaction with the retrieved context. Performance hinges on the synergy of these components.
- Consider Hybrid Approaches: For complex use cases, RAG might be combined with fine-tuning or other techniques to achieve optimal results.
4. Over-reliance on Prompt Engineering Alone & Skipping Robust MLOps
Prompt engineering is crucial, but it’s often viewed as a silver bullet. Organizations might deploy a set of prompts without integrating them into a scalable, maintainable, and monitorable system, leading to fragility and difficulty in production.
What to do instead:
- Integrate into MLOps Pipelines: Treat your Generative AI solution like any other software product. Implement robust MLOps practices for prompt versioning, model deployment, monitoring, and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD).
- Beyond Simple Prompts: While initial prompts are a start, consider using more advanced techniques like Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting, Self-Consistency, or tools like LangChain/LlamaIndex for more complex reasoning and multi-step tasks.
- Build for Scalability and Maintainability: Design your Generative AI applications to be scalable, fault-tolerant, and easy to update. Avoid hardcoding prompts where dynamic generation or external configuration is more appropriate.
5. Skipping Robust Evaluation and Human Oversight
The allure of AI’s autonomy can sometimes lead to premature deployment without adequate testing or a ‘human-in-the-loop’ strategy. Generative AI, especially, can produce convincing but incorrect, biased, or nonsensical outputs (hallucinations).
What to do instead:
- Implement Comprehensive Evaluation Metrics: Go beyond anecdotal evidence. Use automated metrics (e.g., ROUGE, BLEU for text generation) alongside human evaluation for accuracy, relevance, coherence, and safety.
- Establish a Human-in-the-Loop Process: For critical applications, integrate human review and validation workflows. This ensures quality control and helps in fine-tuning the AI’s performance over time.
- Monitor in Production: Continuously monitor your AI system’s outputs, latency, token usage, and user feedback in real-time. Set up alerts for unexpected behavior or performance degradation.
- Prioritize Safety and Ethics: Actively test for biases, toxicity, and potential misuse. Develop guidelines for responsible AI use and output moderation.
Conclusion: Build a Solid Foundation for Generative AI Success
Generative AI is not a magic wand, but a powerful tool that requires thoughtful application. By recognizing and actively addressing these common mistakes, you can lay a much stronger foundation for your Generative AI initiatives. Focus on clear objectives, high-quality data, sophisticated architectural understanding, robust MLOps, and continuous evaluation to truly unlock the transformative power of AI in your organization.